Life Sciences
R& D solutions using generative and image AI, including drug discovery support, image and tissue analysis, quality control, and research DX.

social infrastructure¹. CarbGeM uses generative AI, image AI, and cloud technologies to help solve labor shortages, standardize work, and assist with real-time decision-making. CarbGeM's mission is to support human health and social sustainability, as well as contribute to a better future through technology.
CarbGeM is committed to social implementation through a comprehensive approach that is deeply rooted in life sciences while also encompassing healthcare and other industries, including social infrastructure. By leveraging cutting-edge generative AI, image AI, and cloud technologies, CarbGeM offers innovative solutions to challenges faced by companies and hospitals, such as labor shortages, work standardization, and real-time decision-making.
CarbGeM provides innovative AI solutions in five key areas, with life sciences at its core:
R& D solutions using generative and image AI, including drug discovery support, image and tissue analysis, quality control, and research DX.
Solutions include medical document assistants, AI chatbots, diagnostic imaging support, and health data integration.
Services for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, automated inquiries, FAQ generation, and marketing analysis.
Solutions for anomaly detection, visual inspection, process optimization, predictive maintenance, and advanced capabilities through image analysis and IoT.
Data utilization and decision-making for disaster prevention, urban management, traffic control, and disaster response

Provides an AI chatbot to help patients with follow-ups for lifestyle-related diseases and medication adherence. This reduces the burden on healthcare professionals and improves patient self-care and medication adherence
#Lifestyle-Related Disease Follow-Up #Medication Support Chatbot #Self-Care #Medication Adherence

Helps with QC support, automation, and standardization for cell and regenerative medicine products, including morphological evaluation and label checks. It also supports quality control in the food and cosmetics industries, as well as anomaly detection and efficiency improvement in factories.
#Cell Products #Regenerative Medicine #QC Support #Automation #Standardization #Label Display Check #Labeling Check #Food Cosmetics #Anomaly Detection #Knowledge Sharing #Visualization #Factory Efficiency #Detection Of Subtle Changes

Improves the efficiency and accuracy of R&D and business planning through services like compound and material discovery, literature and intellectual property searches, and clinical trial design. It also helps improve patient quality of life through early detection and intervention.
#Compound Search #Organic Compound Search #Material Search #Literature Search #IP Research #Clinical Trial Design #Early Detection #Early Intervention #Improving Patient QOL

Standardizes and improves the efficiency of lab work through tools like blood cell classification and Gram stain image AI for infectious disease diagnosis support. This facilitates expeditious diagnosis and judicious antibiotic utilization, enhancing healthcare quality.
#Examination Support #Gram Staining Image AI #Infectious Disease Diagnosis #Antimicrobial Stewardship #Rapid Diagnosis
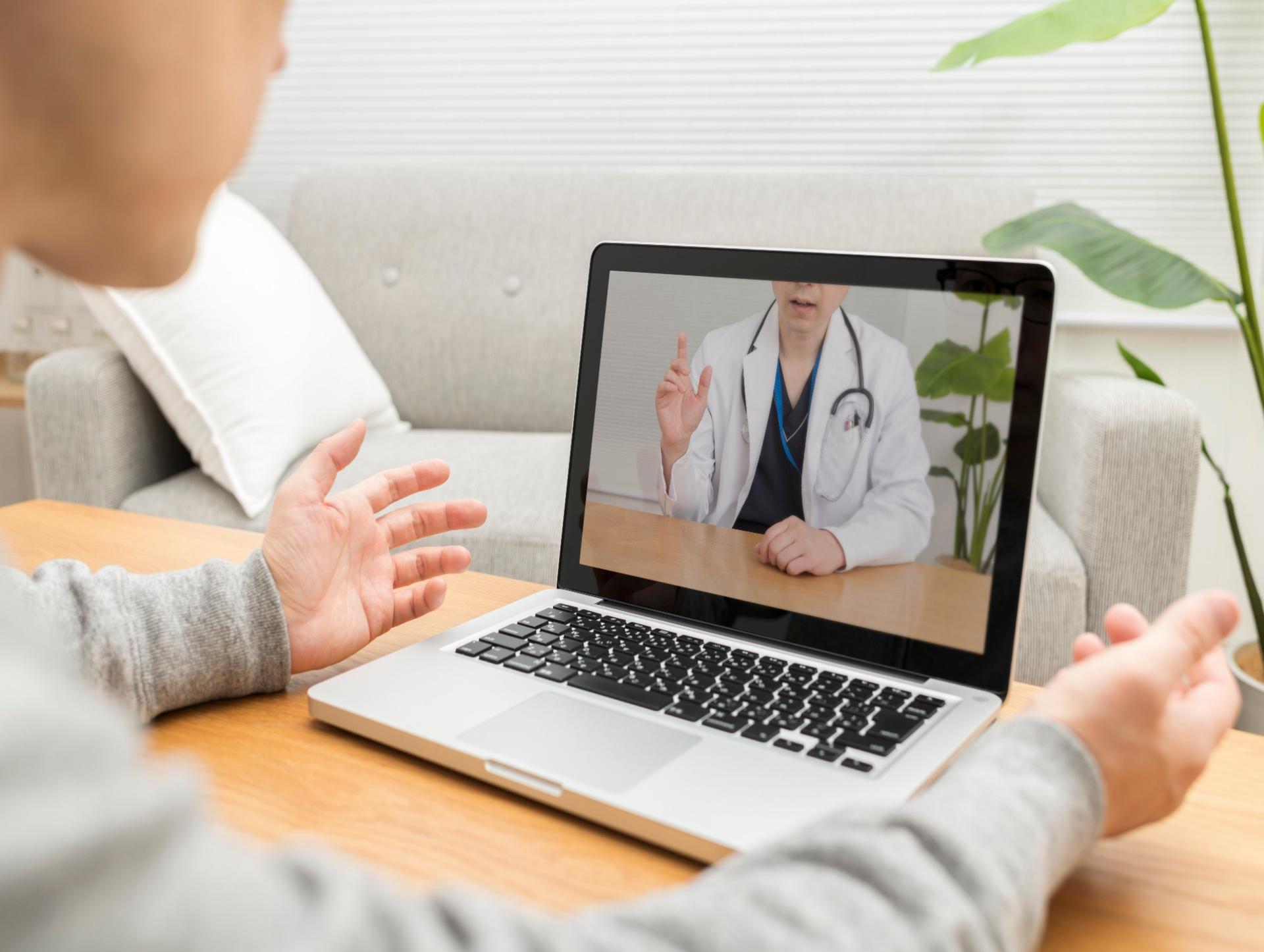

Improve medical access for individuals in remote areas or those working abroad, supporting high-quality healthcare services regardless of geographical constraints.
#Improving Healthcare Access #Supporting Expatriates #Telemedicine #GlobalHealth

Integrate map data with image AI to provide a comprehensive view of social challenges, streamline logistics and routes, and promote knowledge exchange. These capabilities contribute to the enhancement of the sustainability of social infrastructure.
#Issue Visualization #Logistics Optimization #Knowledge Sharing #Route Efficiency
CarbGeM has a team of experts with deep knowledge and extensive experience in fields like cell biology, molecular biology, and medicine. This allows them to accurately understand client challenges and propose optimal solutions.
CarbGeM employs state-of-the-art AI technologies, including image AI, generative AI, and machine learning, to deliver innovative solutions to complex challenges that conventional methods often fail to address.
CarbGeM is equipped to develop flexible solutions tailored to each client's unique needs. Rather than offering standard packages, we provide customized solutions that are optimized for the client's specific workflows and existing systems.
We integrate our expertise in life sciences with state-of-the-art AI technology to assist our clients in addressing challenges and driving operational innovation. We contribute to building a better society by addressing labor shortages, standardizing work processes, and enabling real-time decision support
From the inquiry form below, please fill in the required fields,
and feel free to contact us.